Archives
- 2026-03
- 2026-02
- 2026-01
- 2025-12
- 2025-11
- 2025-10
- 2025-09
- 2025-03
- 2025-02
- 2025-01
- 2024-12
- 2024-11
- 2024-10
- 2024-09
- 2024-08
- 2024-07
- 2024-06
- 2024-05
- 2024-04
- 2024-03
- 2024-02
- 2024-01
- 2023-12
- 2023-11
- 2023-10
- 2023-09
- 2023-08
- 2023-07
- 2023-06
- 2023-05
- 2023-04
- 2023-03
- 2023-02
- 2023-01
- 2022-12
- 2022-11
- 2022-10
- 2022-09
- 2022-08
- 2022-07
- 2022-06
- 2022-05
- 2022-04
- 2022-03
- 2022-02
- 2022-01
- 2021-12
- 2021-11
- 2021-10
- 2021-09
- 2021-08
- 2021-07
- 2021-06
- 2021-05
- 2021-04
- 2021-03
- 2021-02
- 2021-01
- 2020-12
- 2020-11
- 2020-10
- 2020-09
- 2020-08
- 2020-07
- 2020-06
- 2020-05
- 2020-04
- 2020-03
- 2020-02
- 2020-01
- 2019-12
- 2019-11
- 2019-10
- 2019-09
- 2019-08
- 2019-07
- 2019-06
- 2019-05
- 2019-04
- 2018-07
-
br The complementary role of chaperone mediated autophagy Ch
2024-12-18
The complementary role of chaperone mediated autophagy Chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA) mediates the degradation of specific cellular proteins and participates in the regulation of lipid metabolism, DNA repair, or the response to stress (Kaushik and Cuervo, 2018). CMA provides an alternative pa
-
quercetine Compound was docked into the active site of Auror
2024-12-18
Compound was docked into the active site of Aurora B kinase using Tripos sybyl-X ver. 2.1.1. The crystal structure of human Aurora B kinase cocrystallized with its potent inhibitor VX-680 was used for the docking analysis (PDB ID: ). The most likely binding conformations were selected based on the
-
We have recently reported a
2024-12-18
We have recently reported a regulatory effect of quercetin on the AChE activity in the brainstem during the demyelination and remyelination process [17]. It has also been observed that there is a protective effect on lipid peroxidation and worsening of motor functions caused by loss of myelin in the
-
Because R gene is positively regulated by T
2024-12-18
Because 5α-R2 gene is positively regulated by T and in the prostate gland (Torres et al., 2003), and our BPA-treated rats showed decreased circulating T and probably intraprostatic androgen levels, it might be responsible for the decrease of 5α-R2 expression. However, in a previous work using castra
-
On the contrary Birrel and
2024-12-17
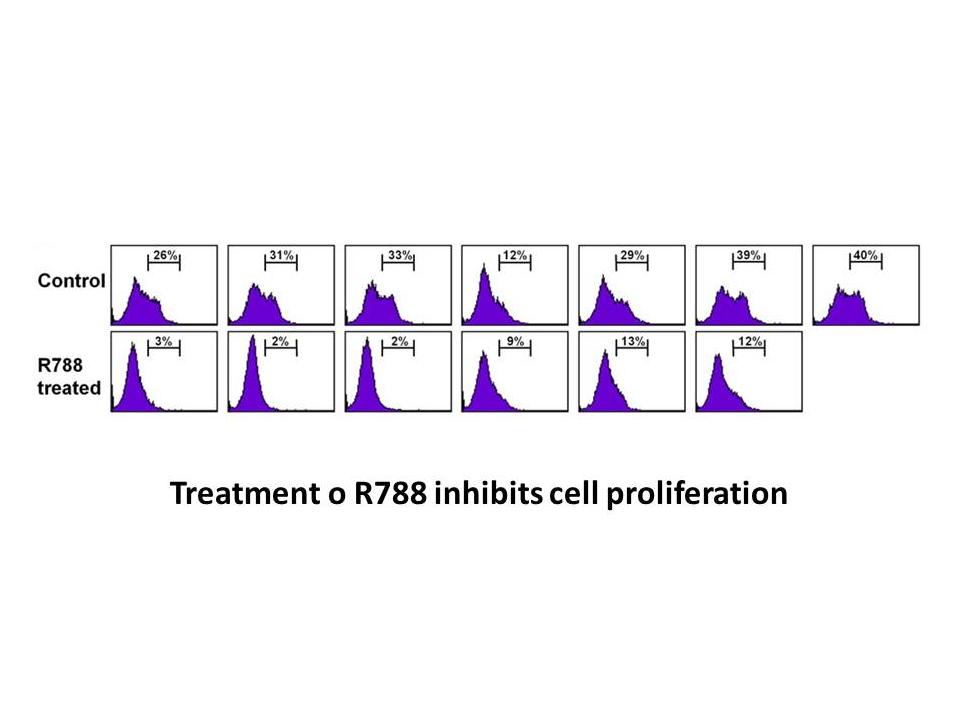
On the contrary, Birrel and colleagues observed divergent proliferative responses to androgens in different BC cell lines: DHT and mibolerone were found to inhibit the T47-D and ZR-75-1 Biotin-azide growth, while the proliferation of MCF-7 cells was increased by both the androgens [53]. It is worth
-
The G R mutation is located at the solvent
2024-12-17
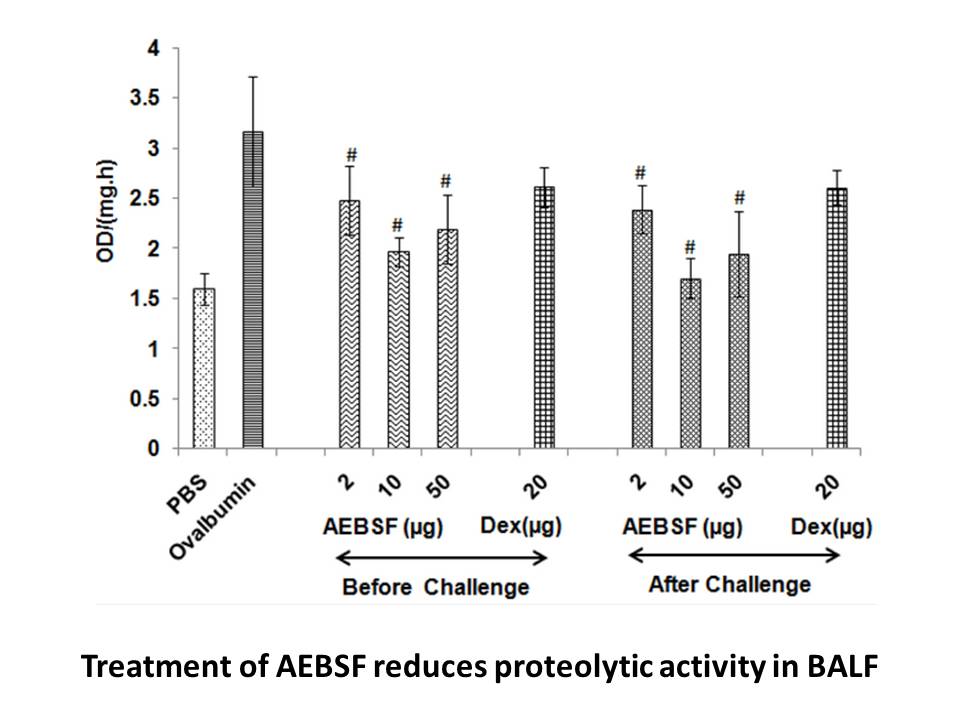
The G1202R mutation is located at the solvent front of the ALK kinase domain adjacent to the inhibitor's binding pocket. Although barely reported in the setting of crizotinib resistance, it has emerged as the most refractory mutation to both the first- and second-generation ALK inhibitors. The large
-
The observation that vortioxetine blocks HT induced currents
2024-12-17
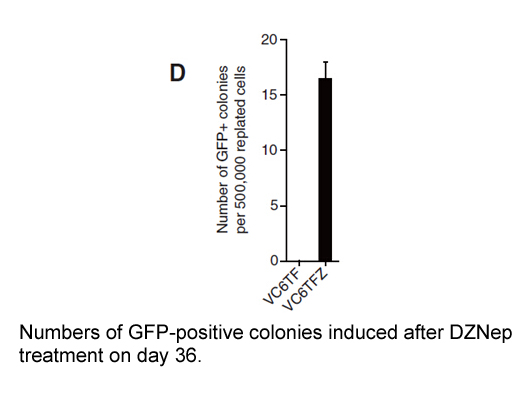
The observation that vortioxetine blocks 5-HT-induced currents in 5-HT3 receptor-expressing oocytes suggests that vortioxetine acts to functionally antagonize these receptors, and is in line with previously published data (Bang-Andersen et al., 2011). For example, Mørk et al. (2012) demonstrated tha
-
The second evidence comes from the results obtained by
2024-12-17
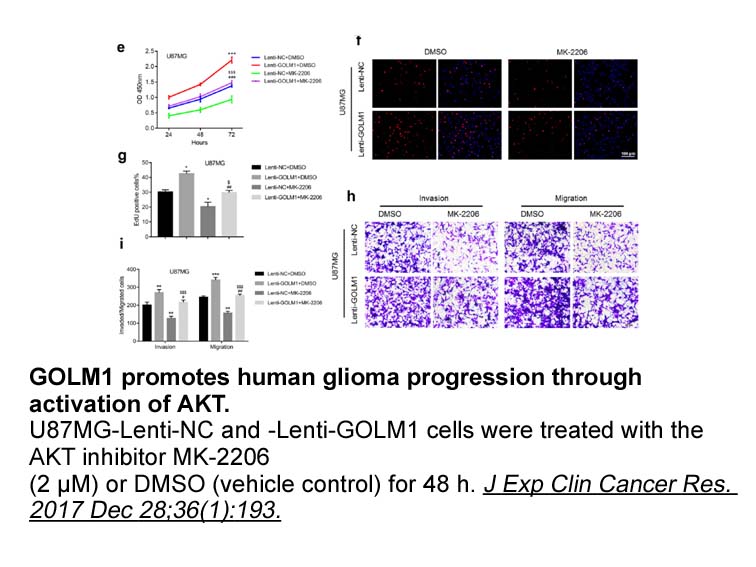
The second evidence comes from the results obtained by patch-clamp recordings carried out at the endplate region of isolated mouse FDB fibers, where adenosine and the P1R agonist NECA significantly affected the NPo, the open frequency and the time constant τ of the adult nAChR channels. It is genera
-
br Introduction br Rac dependent ROS and
2024-12-17
Introduction Rac1-dependent ROS and BMS265246 receptor regulation in neuronal functions NOX-mediated ROS have an important role as physiological messengers. One remarkable example regarding such a function is during axonal formation. In this line, increased p40phox/NOX2 levels and co-localiza
-
Introduction The lysosomal storage disorder Gaucher disease
2024-12-17
Introduction The lysosomal storage disorder Gaucher disease (Mendelian Inheritance in Man, OMIM #230800) results from the recessively inherited deficiency of lysosomal glucocerebrosidase (GCase, EC 3.2.1.45), caused by mutations in the gene GBA1 (MIM# 606463) located on chromosome 1q21. The enzymat
-
rs G allele was previously associated with
2024-12-17
rs523349 G allele was previously associated with a decrease in the conversion rate of testosterone to DHT (Beesley et al., 2007). This SRDA52 variant may have a trend towards higher testosterone availability, which according to the US Food and Drug Administration is described as a teratogen of categ
-
Whole body loss of ACLY
2024-12-16
Whole-body loss of ACLY is early embryonic lethal, indicating that it serves non-redundant roles during development (Beigneux et al., 2004). Silencing or inhibition of ACLY suppresses the proliferation of many cancer cell lines and impairs tumor growth (Bauer et al., 2005, Hanai et al., 2012, Hatziv
-
br Materials and methods br Results and discussion
2024-12-16
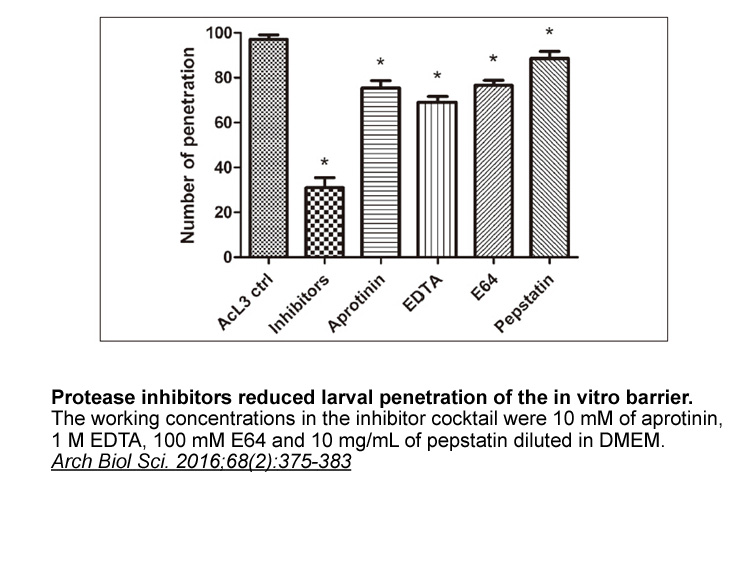
Materials and methods Results and discussion During recent years, recombinant ASK1 has been obtained by expensive baculovirus-insect cell DC260126 mg systems [20], [27]. In the present study, we constructed recombinant ASK1 and expressed in active form at high level in E. coli. Human ASK1 ca
-
According to the diversity in molecular skeletons aromatase
2024-12-16
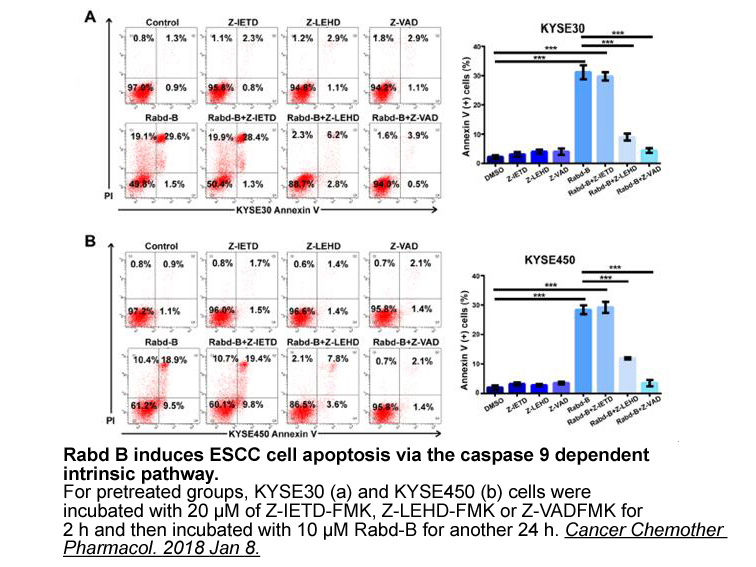
According to the src inhibitors in molecular skeletons, aromatase inhibitors can be categorized into two types: steroidal and non-steroidal blockers [6]. Steroidal AI (e.g., exemestane in Fig. 1) derived from the substrate androstenedione interacts with aromatase through chemical actions, resulting
-
br Conflict of interest br Acknowledgment The
2024-12-16
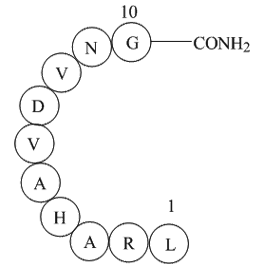
Conflict of interest Acknowledgment The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (81070220 and 81170278), and the Aid Program for Science and Technology Innovative Research Team in Higher Educational Institutions of Human Provi
16124 records 44/1075 page Previous Next First page 上5页 4142434445 下5页 Last page